New research presents a map to begin 2021 in a heart-wholesome way
If you’re making resolutions for 2021, why not make a person that’s very good for your heart?
A new analyze by researchers from Northeastern College, Harvard College, and Brigham and Women’s Medical center displays that certain foods—including wine, yogurt, carrots, peanuts, breakfast cereal, grapes, and raisins—are affiliated with a lower hazard of establishing coronary heart condition.

Left to ideal: Soodabeh Milanlouei, a graduate pupil in industrial engineering, Albert-László Barabási, Robert Gray Dodge Professor of Community Science and College Distinguished Professor of physics and Giulia Menichetti, an affiliate investigation scientist at Northeastern’s Heart for Complicated Network Analysis. Pictures by Adam Glanzman and Matthew Modoono/Northeastern University
The scientists also located numerous foodstuff that were linked with an greater possibility of establishing heart sickness, together with processed meat, doughnuts, and white bread.
“Diet-induced conditions are the major supply of death in the U.S.,” suggests Albert-László Barabási, Robert Gray Dodge Professor of Community Science and college distinguished professor of physics at Northeastern, and one of the researchers in the research.
“It is vital, therefore, to deliver new instruments to achieve insights into the vitamins and the foods that have an adverse impact on wellbeing,” he says.
Almost everything we consume, from yogurt to doughnuts, is made up of thousands of diverse chemical compounds that could have an affect on our wellbeing. Barabási and his colleagues—including Giulia Menichetti and Soodabeh Milanlouei, scientists at Northeastern’s Centre for Advanced Network Investigation—have been painstakingly pinpointing and tracking these chemical compounds in our foodstuff.
Every thing we take in, from yogurt to doughnuts, contains hundreds of distinctive chemical compounds that could affect our wellbeing. Knowledge visualization by Albert-László Barabási, BarabasiLab 2020.
Final 12 months, they documented extra than 2,000 chemical compounds in garlic by itself, 485 of which are however unquantified in food composition databases, even with their opportunity wellness results.
But we do not eat these chemical compounds in a vacuum, Menichetti claims. If we’re mincing garlic to include to an aioli, we’re eventually eating all the chemicals in garlic at as soon as, as well as those uncovered in the other components, such as egg yolk and lemon juice, and their byproducts. And these nutrients—some of which may possibly be found in a number of distinctive foods—may have distinct effects on our health and fitness, relying on where by they occur from and the foods in which they are eaten, she claims.
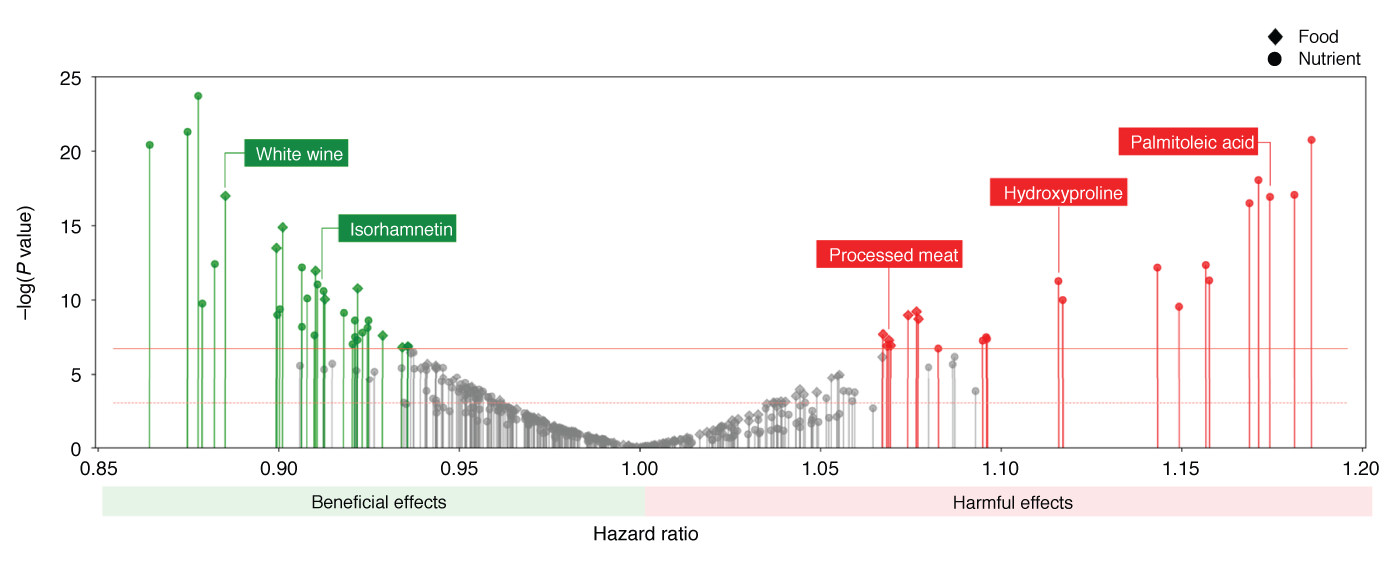
They explored the affiliation of 257 vitamins and 117 meals with coronary coronary heart disease working with info from the Nurses’ Wellbeing Review, a nationwide study that adopted the feeding on patterns and health outcomes of roughly 63,000 girls around 30 a long time. Courtesy graphic.
So for this analyze, Menichetti, Milanlouei, Barabási, and their teammates—Yanping Li and Walter C. Willett from Harvard University, and Joseph Loscalzo from Brigham and Women’s Hospital— wielded the electrical power of major facts and computation to research the health penalties of food items and vitamins and minerals all at at the time.
They explored the affiliation of 257 nutrition and 117 foodstuff with coronary coronary heart disorder applying details from the Nurses’ Wellness Examine, a national study that adopted the consuming designs and wellbeing outcomes of about 63,000 women in excess of 30 decades. The survey is currently in its third iteration and amongst the largest of this sort of investigations. Menichetti describes it as “the gold regular for epidemiological studies.”
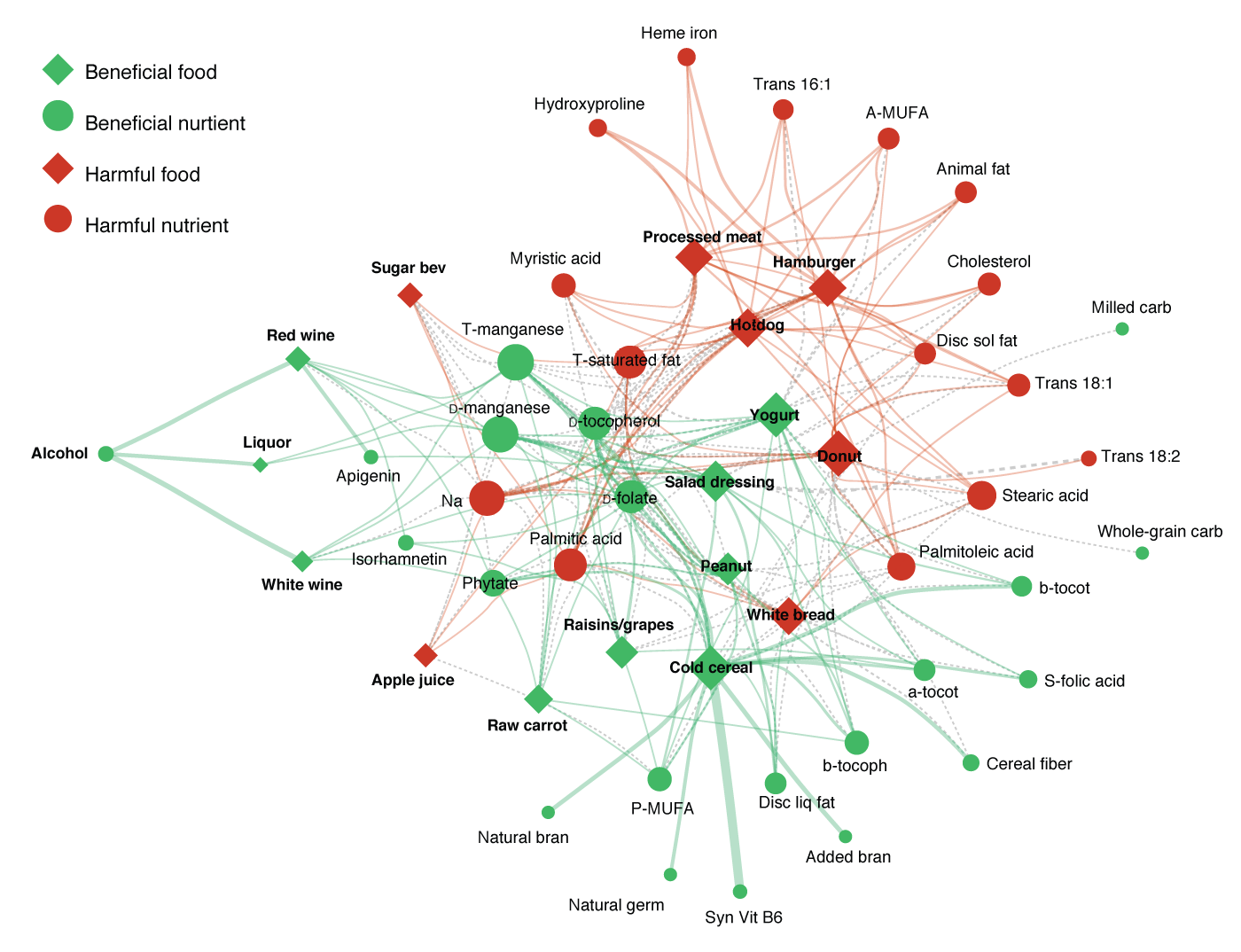
The researchers screened the meals and vitamins and minerals from overall health implications to search for statistically major correlations. Sixteen food items and 37 nutrients confirmed solid correlations—some of which have been related with a increased hazard of creating coronary heart ailment and some with a decreased danger.
Their analysis revealed that some vitamins, this kind of as full grain carbohydrates and milled total grain carbohydrates, experienced distinctive possibility variables dependent on the foods in which they have been found.
White bread and processed meats include these vitamins and minerals and had been found to increase the danger of coronary heart disease. Cold breakfast cereals and raw carrots also incorporate these nutrients, yet were identified to lower the chance.
It’s an illustration of the benefits of the researchers’ holistic assessment.
“Our assessment offers some duty to the composition of our food items supply,” she says. “We can teach folks to have greater weight loss plans, but we also have to strengthen the foodstuff offer itself.”
The researchers expect that this analyze will blaze the path for potential investigations into the complicated romance concerning meals and wellbeing. Still, they accept various limitations in their perform. Initial, the Nurses’ Overall health Analyze is composed only of women of all ages who are nurses. 2nd, the examine targeted strictly on the connection amongst diet plan and coronary heart illness, devoid of thing to consider for the rest of the setting in which a particular person life.
Nonetheless, the new findings reveal a “tangible effect” of a person’s diet on their coronary heart well being, Milanlouei states.
And the success are currently changing some people’s behavior—Menichetti says the doctoral pupils operating in Barabási’s lab have built “drastic changes” to their diet plans as a result of this get the job done.
“Way much less processed foods,” she says. “A good deal of folks have started off cooking with contemporary food items yet again.”
For media inquiries, you should call Marirose Sartoretto at [email protected] or 617-373-5718.
